OOP_01
Just a note
4 tính chất:
1. Encapsulation (tính đóng gói):
Procedural: f(x,y,z)
OOP: bind { [(x,y,z) = property] + [f = method] } = Class
Why?
Encapsulation is an object-oriented programming concept that binds together the data and functions that manipulate the data, and that keeps both safe from outside interference and misuse. Data encapsulation led to the important OOP concept of data hiding.
If a class does not allow calling code to access internal object data and permits access through methods only, this is a strong form of abstraction or information hiding known as encapsulation. Some languages (Java, for example) let classes enforce access restrictions explicitly, for example denoting internal data with the private keyword and designating methods intended for use by code outside the class with the public keyword. Methods may also be designed public, private, or intermediate levels such as protected (which allows access from the same class and its subclasses, but not objects of a different class). In other languages (like Python) this is enforced only by convention (for example, private methods may have names that start with an underscore). Encapsulation prevents external code from being concerned with the internal workings of an object. This facilitates code refactoring, for example allowing the author of the class to change how objects of that class represent their data internally without changing any external code (as long as "public" method calls work the same way). It also encourages programmers to put all the code that is concerned with a certain set of data in the same class, which organizes it for easy comprehension by other programmers. Encapsulation is a technique that encourages decoupling.
[Wiki]: manipulate the data, and that keeps both safe from outside interference and misuse.
- Safe from outside:
Other objects do not have access to this class or the authority to make changes but are only able to call a list of public methods. This characteristic of data hiding provides greater program security and avoids unintended data corruption.
Ví dụ: [C++]
class Account {
private: double balance = 100;
};
int main(){
Account myAcc;
myAcc.balance = 200;
return 0;
}
Kết quả:
error: ‘double Account::balance’ is private within this context
myAcc.balance = 200;
^~~~~~~
- Misuse.
Như hình dưới, hàm getWage được truyền vào 3 tham số . Trong quá trình phát triển, nêu hàm này thêm một tham số nữa, hoặc thay tham số này bằng tham số khác, đoạn code còn lai sư dụng hàm này cũng phải thay đổi theo, nếu không sẽ dẫn đên misuse
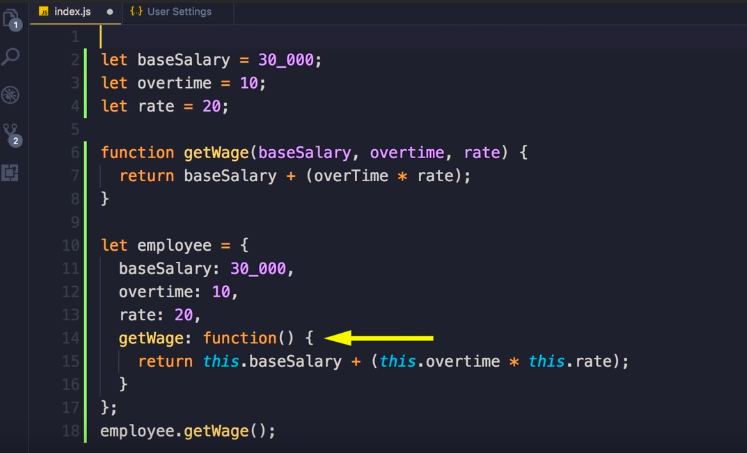
Prob:
- Tính đóng gói trong procedural lang, scope?
- private, public, protected và ?
2. Abstraction (tính trừu tượng):
(What is Abstraction in OOPS?)[https://www.journaldev.com/33191/what-is-abstraction-in-oops]
Why?
- Simpler Interface
Thao tác trên một Object có ít property và method sẽ hiệu quả hơn nhiều - Reduce the impact of change
Khi tác động vào những property và method đã bị ẩn đi ấy, sẽ không ảnh hưởng đến toàn bộ code còn lại bên ngoài, đảm bảo được tính toàn vẹn.
Prob:
3. Inheritance (tính thừa kế ):
Why?
Eliminate redundant code
Prob:
- How?
- lớp con thừa kế lớp cha, có những đặc quyền gì?
- lớp cha có được thừa kế lớp con không? vì sao?
- đa thừa kế và đơn thừa kế?
- những ngôn ngữ nào đa thừa kế và những ngôn ngữ nào không?
4. Polymorphism (tính đa hình)
Why?
Poly = Many
Morph = Form
Polymorphism = Đa hình = Mỗi form sẽ có môt cách thức xử lý các hàm khác nhau.
Subtyping – a form of polymorphism – is when calling code can be agnostic as to which class in the supported hierarchy it is operating on – the parent class or one of its descendants. Meanwhile, the same operation name among objects in an inheritance hierarchy may behave differently.
Ví dụ khi định nghĩa hai đối tượng "hinh_vuong" và "hinh_tron" thì có một phương thức chung là "chu_vi". Khi gọi phương thức này thì nếu đối tượng là "hinh_vuong" nó sẽ tính theo công thức khác với khi đối tượng là "hinh_tron".
For example, objects of type Circle and Square are derived from a common class called Shape. The Draw function for each type of Shape implements what is necessary to draw itself while calling code can remain indifferent to the particular type of Shape is being drawn.
Ví dụ: Operator + trong JavaScript:
4 + 4 = 8
'Hello ' + 'World' = 'Hello World'
'Hello ' + 44 = 'Hello 44'
Ta nói, phép + có tính đa hình.
Khi môt object adapt được với những bôi cảnh khác nhau ta nói object đó có tính đa hình.
Prob:
- How?
Tham khảo:
1.Object-oriented Programming in 7 minutes
2.Object Oriented Polymorphism
3.Object Oriented Programming